Table of Contents
- Summary
- Introduction
- What is Parameterization in JMeter?
- Techniques for Parameterization in JMeter
- Using CSV Data Set Config
- Using User Defined Variables
- Using Property Files / Environment Variables
- Using Database Data through JDBC
- Best Practices for Parameterization
- What is Correlation in JMeter?
- Difference between parameterization and correlation
- Why correlation is needed in dynamic applications
- Techniques for Correlation in JMeter
- Using Regular Expression Extractor
- Using JSON Extractor
- Using Boundary Extractor
- Handling Dynamic Values in Requests
- Automated Tools for Correlation
- Configuring “CSV Data Set Config” parameters
- 1. Name
- 2. Filename
- 3. File Encoding
- 4. Variable Names
- 5. Delimiter
- 6. Allow Quoted Data?
- 7. Recycle on EOF?
- 8. Stop Thread on EOF?
- 9. Sharing Mode
- Steps to add elements in Jmeter
- Step 1:
- Step 2:
- Step 3:
- Step 4:
- Step 5:
- Step 6:
- For User1:
- Common Challenges & Best Practices
- Avoiding Script Failures Due to Missing Correlations
- Keeping Parameter Files Secure
- Validating Extracted Values
- Reusability and Maintainability of Test Scripts
- About QSS
- How QSS Technosoft Helps
- About Author
- Conclusion
- FAQs Section
Summary
Parameterization and correlation are the backbone of effective performance testing in JMeter. While parameterization enables dynamic data handling by fetching user inputs from external sources like CSV files, correlation ensures proper session handling by capturing and reusing dynamic server values such as tokens or IDs. Together, they make test scripts scalable, realistic, and reliable, closely mimicking real-world user behavior. Implementing these techniques helps avoid errors, ensures accuracy, and improves script maintainability. With proper practices like secure data handling, validation, and modular scripting, performance testing becomes more robust. Partnering with experts like QSS Technosoft ensures end-to-end implementation of parameterization and correlation strategies, delivering optimized and enterprise-ready test outcomes.The performance of applications can be affected by factors like server capacity and network latency.
Introduction
Parameterization is used for fetching the values from the CSV file. It is used, when we want to run a script with a different set of users. Through CSV files, we can get a large amount of data that can be used for the script. JMeter is widely used for performance testing web applications. You can also specify a default value for variables in case the CSV file has missing or empty entries. These values are stored as JMeter variables, which can then be referenced throughout the test plan to simulate different user inputs dynamically.
For example, If we want to run sign up a script for 100 users, then it might throw an error for a unique Email ID and Username, if not met against the unique parameters required in the website. To overcome this problem, you need to fetch values from the CSV file by naming the following variables as a column header in the CSV file. You can also specify a default value for variables in case the CSV file has missing or empty entries. So parameterization comes into play when we want a Test Plan with a different set of users at the same time.
Correlation is used to extract value from a HTTP request. For this, we make use of processors which could be pre-processors or post-processors. In most cases, we make use of post-processors. This can be XPath and Regular Expression Extractor. These are used to extract value from the response and store the value in any variable which can be later used in any request. For example, it can be used for Session ID, cookies value, or a random value. A key request in the test flow often requires correlation to handle dynamic parameters correctly.
What is Parameterization in JMeter?
Parameterization in JMeter is the process of replacing hard-coded values in test scripts with variables that can take different data inputs during test execution. Its purpose is to make performance tests dynamic and scalable by allowing the same test plan to simulate multiple users or scenarios with varying data sets using JMeter variables.
This approach avoids hard-coding values like usernames or passwords, which would otherwise limit the test's flexibility. For example, in a login test, parameterization enables running the script for multiple users by fetching different credentials from a CSV file, thereby simulating real-world usage where each user logs in with unique information.
Techniques for Parameterization in JMeter
Using CSV Data Set Config
The CSV Data Set Config element is one of the most popular and effective techniques for parameterization in JMeter. It allows you to read data from an external CSV file and use those values as variables in your test scripts.
This approach is ideal for running tests with multiple users or different input data sets, such as login credentials or search terms. By specifying the file path, variable names expression , delimiter, and other settings, you can easily manage dynamic test data and ensure your tests simulate real-world scenarios.
Using User Defined Variables
User Defined Variables provide another way to parameterize your JMeter test plans. These are variables that you define directly within your test plan, allowing you to reuse values across multiple requests or thread groups. They also enable you to evaluate nested variable references, enhancing the flexibility of your test scripts.
This method is useful for static or semi-static data that doesn't change frequently during test execution. User Defined Variables can also be combined with other parameterization techniques to enhance flexibility and maintainability.
Using Property Files / Environment Variables
JMeter supports parameterization through property files and environment variables, enabling you to externalize configuration and dynamic data. Property files allow you to define key-value pairs that can be referenced throughout your test plan using property functions.
Environment variables can be accessed similarly, making it easier to manage different test environments or sensitive data like passwords without hardcoding them into scripts. This technique promotes better separation of test logic and configuration.
Using Database Data through JDBC
JMeter allows parameterization using database data via JDBC requests. First, configure the database connection using the 'JDBC Connection Configuration' element by specifying the database URL, driver class, username, and password.
Then, add a 'JDBC Request' sampler to execute SQL queries that fetch dynamic test data. Extracted values from the database can be stored in variables and used in subsequent requests, enabling tests to simulate real user data stored in databases.
Empower Your Digital Vision with an Award-Winning Tech Partner
QSS Technosoft is globally recognized for innovation, excellence, and trusted delivery.
- Clutch Leader in App Development 2019
- Ranked Among Top 100 Global IT Companies
- Honored for Cutting-edge AI & Mobility Solutions
Best Practices for Parameterization
When parameterizing your JMeter tests, it is important to maintain clarity and scalability. Use descriptive variable names to improve readability and avoid confusion. Always validate that the data files (like CSVs) are correctly formatted and accessible during test execution.
Recycle data appropriately to prevent test failures due to data exhaustion, and consider thread group safety when sharing variables across threads. Combining multiple parameterization techniques can provide a robust and flexible test plan that simulates realistic user behavior and delivers reliable test results. Additionally, managing the thread count effectively ensures optimal resource utilization and accurate load simulation during performance testing.
What is Correlation in JMeter?
Correlation extracts dynamic values generated by the server, such as session IDs, tokens, or timestamps, which change with each interaction. By capturing and reusing these values, JMeter correlation maintains the continuity and validity of user sessions during load testing. It is significant because it enables test scripts to adapt to dynamic responses, ensuring reliable and accurate performance testing results. Manual correlation plays an important role in correlation process, where testers explicitly define extraction rules and variables to handle dynamic values correctly.
It ensures that test scripts handle changing data like session IDs and authentication tokens correctly. This makes the test realistic and prevents failures caused by invalid or expired data. JMeter correlation, including the use of auto correlation techniques, is essential for maintaining valid user sessions and accurate simulation of real user behavior. Auto correlation tools can significantly simplify the correlation process by automatically identifying and handling dynamic values, reducing manual errors and saving time.orrelation is essential for maintaining valid user sessions and accurate simulation of real user behavior.
Difference between parameterization and correlation
Parameterization and correlation are closely related but serve distinct functions in performance testing with JMeter correlation . Parameterization focuses on substituting hard-coded input values in the test scripts with variables that can represent multiple data sets.
This allows simulating different users or scenarios by feeding various inputs dynamically during test execution. The values for parameterization often come from external sources like CSV files, property files, or user-defined variables within the test plan. It primarily deals with input data that testers control and define beforehand. Parameterization can be combined with manual correlation techniques, such as using a regular expression extractor, to handle dynamic server responses, or enhanced by auto correlation tools that automate the extraction and reuse of dynamic values, making test script creation more efficient and less error-prone.
Correlation, on the other hand, is concerned with handling dynamic values generated by the server during test execution. These values, such as session IDs, authentication tokens, or timestamps, change with every user interaction or request.JMeter correlation plays a crucial role in this process by extracting and managing these dynamic values to ensure accurate and reliable test execution. Using automated tools and best practices can make jmeter correlation easier, reducing manual errors and saving time.
Correlation involves extracting these dynamic values from server responses using post-processors like Regular Expression Extractors, JSON Extractors, or Boundary Extractors, and then injecting them into subsequent requests to maintain valid sessions and realistic user flows.
While parameterization makes the test data-driven and scalable by using multiple sets of input data, correlation ensures that the test script adapts to the dynamic nature of the application under test by correctly managing server-generated values.
Both processes are essential for creating robust, reliable, and realistic performance tests. Without parameterization, tests would be limited to static data, and without correlation, tests would fail to handle dynamic session data, leading to errors and inaccurate results.
Understanding the distinction between these two concepts helps testers implement effective test plans that can handle the complexities of modern web applications, ensuring accurate simulation of real user behavior and reliable test outcomes.
Why correlation is needed in dynamic applications
Dynamic applications generate unique values like session IDs and authentication tokens for each user session to maintain security and state. Without correlation, test scripts would reuse stale or invalid dynamic values, causing authentication failures or session errors. Correlation ensures these dynamic values are extracted and passed correctly between requests, enabling realistic and successful load testing of dynamic applications.
Techniques for Correlation in JMeter
Using Regular Expression Extractor
The Regular Expression Extractor is a widely used post-processor in JMeter for correlation. It parses response data using defined regular expressions to extract dynamic values like session IDs or authentication tokens. These extracted values are stored in variables, which can then be referenced in subsequent requests to maintain valid sessions and ensure the test script works properly.
Using JSON Extractor
The JSON Extractor is specifically designed to handle JSON formatted response data. It enables testers to extract values by specifying JSON Path regular expressions, making it easier to capture dynamic data from APIs or web services returning JSON. This method simplifies correlation when dealing with modern RESTful services that frequently use JSON for data exchange.
Using Boundary Extractor
The Boundary Extractor is another post-processor that extracts dynamic values based on left and right boundary strings in the response data. It is useful when the exact pattern for extraction is hard to define using regular expressions but the surrounding text is consistent. This extractor captures the value between specified boundaries and stores it in a variable for reuse.
Handling Dynamic Values in Requests
Handling dynamic values in JMeter requests involves identifying parameters that change with each session, such as tokens or IDs, and correlating them properly. This process requires extracting these dynamic values from previous responses and injecting them into subsequent requests. Proper handling ensures the test script simulates real user behavior and prevents failures due to invalid or expired data.
Automated Tools for Correlation
Automated tools like BlazeMeter's Auto Correlation plugin simplify the correlation process by automatically identifying dynamic values and suggesting variable replacements. These tools reduce the time-consuming manual correlation efforts and minimize errors. They also provide features like correlation recorders and replay capabilities to ensure accurate and reliable test scripts. Using automation makes handling complex dynamic data in JMeter much easier and more efficient. The correlation recorder is a valuable feature that helps testers capture and manage dynamic values effectively. By using a correlation recorder, you can streamline the correlation process and reduce manual errors in your test scripts.
Configuring “CSV Data Set Config” parameters
It is used to read values from the data file, which can be later used as Test data while executing a JMeter script.
1. Name
To change the name of CSV Data Set Config which will be used in the left side of Tree.
2. Filename
It is the name of the CSV file. If this file exists in the bin folder then the only name of the file is required else the full path of the file is required.
3. File Encoding
It is used to read the file
4. Variable Names
These consists of all the variable names, which will be used in the CSV file. These are separated by commas. If this input field is empty then Jmeter will take the 1st row of data as the column name.
5. Delimiter
It is used to separate values in a CSV file, a comma is a default delimiter.
6. Allow Quoted Data?
If it is enabled then it will take value from CSV file which is doubled quoted, by default it is set to false.
7. Recycle on EOF?
It is default set to true which means that once all the set of data is used then it will place the cursor to the beginning of data file for repeating the process.
8. Stop Thread on EOF?
Once the whole set of data is used from CSV then JMeter script will stop if it is set as True. This setting is particularly important when you want each thread group to handle its own data independently during test execution.
9. Sharing Mode
It signifies what all be shared between the threads.
- All threads: If you want to share the file with all threads
- Current thread group: It can be used by each thread group once.
- Current thread: CSV file will be used separately by each thread.
- Identifier: Threads, which are using the same identifier will use the same file
Steps to add elements in Jmeter
Step 1:
a. Adding thread group (Login Script) in Test plan
b. Adding HTTP request Defaults
c. Adding CSV Data Set Config
d. Adding listener as Summary Report to capture the output of JMeter
A JMeter screen will look like this with CSV Data Set Config elements
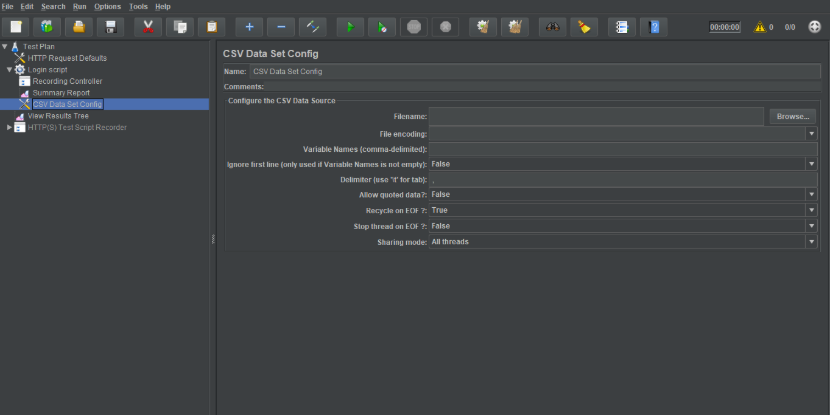
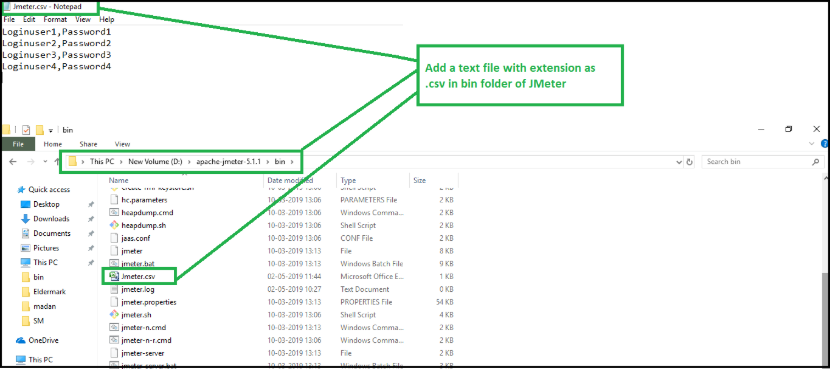
Step 2:
Add a text file with the extension as .csv in the bin folder of JMeter or you need to copy the absolute path of this file in the filename field in the above image.
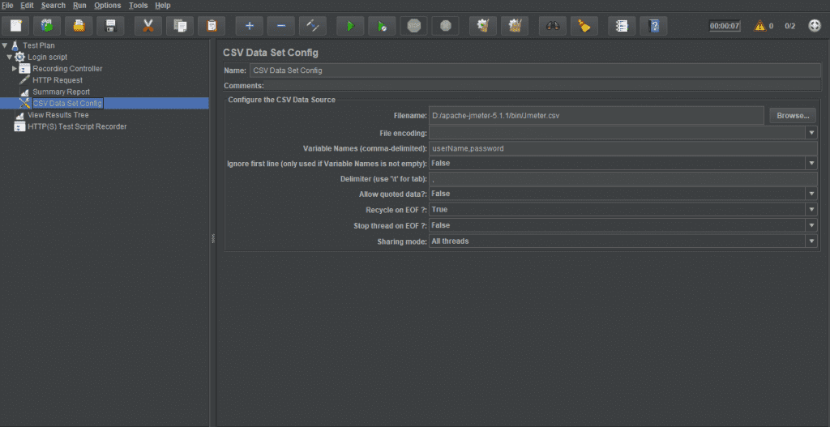
Step 3:
In CSV Data Set Config: Add the same file in Filename field and pass the variable name as username & password
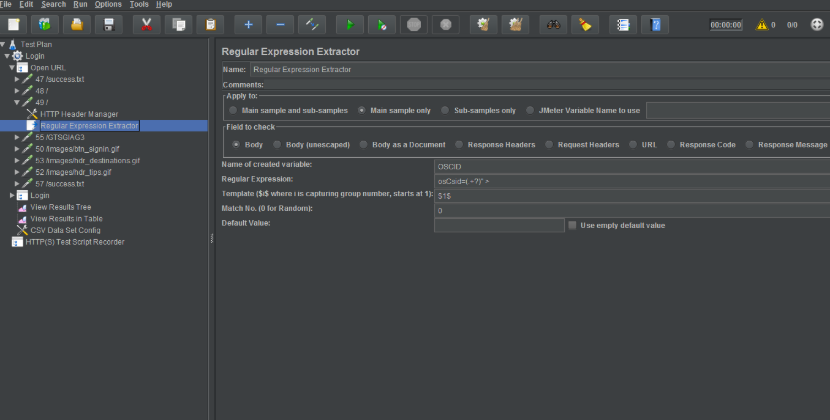
Step 4:
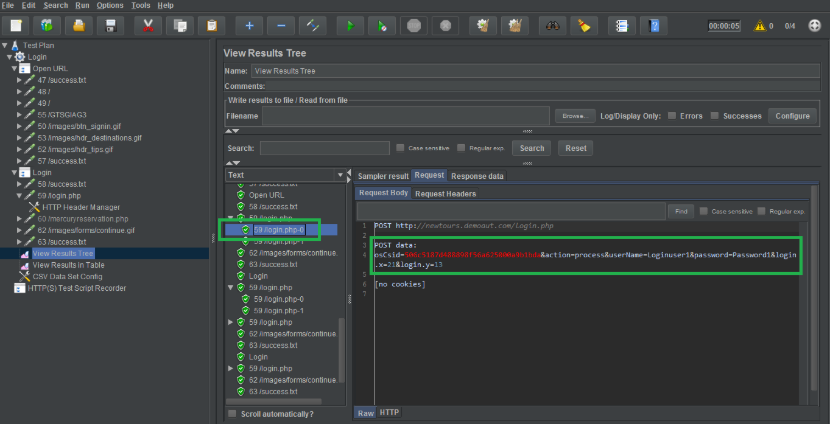
When we record a script, then it stores dynamic values which will not be valid when you execute it next time. As it expired for the next execution or for the next run it needs a new dynamic value e.g. session id, token key, etc.
In the below screenshot, I have used a regular expression extractor for the session ID. Its value is given in the HTTP request in Step 5. If you are not sure which values are changing at each run, you can compare the recorded script Vs the new script value. You will observe that there are some values that are changing each time.
Step 5:
On HTTP Request window, add the value of parameters in Send Parameters With the Request section in the value column as shown below in the image for userName field: ${userName } , password field: ${password} and osCsid field as ${OSCID}.
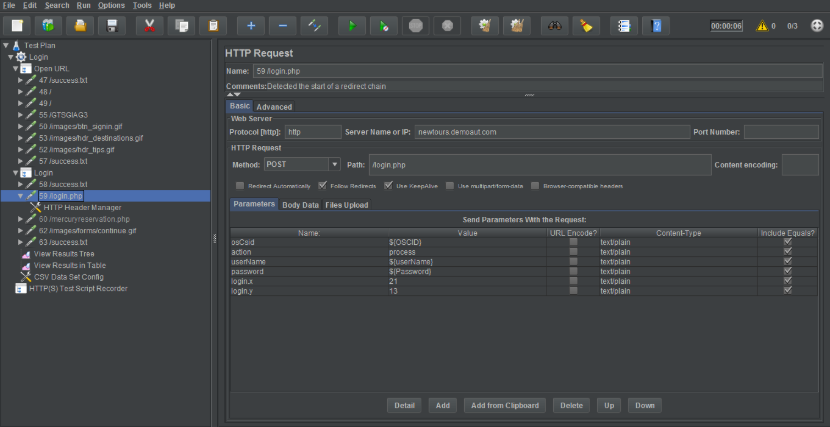
Step 6:
Now based on the thread added in a jmeter.csv file, for example, lets run the script for 4 threads and set the value in Thread group as 4. Now, run this script with the above HTTP request. It will take parameters from Jmeter.csv file.
For User1:
When the script runs, User 1 details will be sent in a request, next User 2 details will be sent and so on till the script runs for User 4.
Common Challenges & Best Practices
Avoiding Script Failures Due to Missing Correlations
One common challenge in performance testing is script failures caused by missing correlations. When dynamic values like session IDs or authentication tokens are not properly extracted and reused, the test scripts may fail or produce unreliable results.
To avoid this, it is essential to carefully identify all dynamic parameters during test recording and implement appropriate correlation techniques such as regular expression extractors or JSON extractors.
Keeping Parameter Files Secure
Parameter files, such as CSV files containing user credentials or sensitive data, must be kept secure to prevent unauthorized access. Best practices include restricting file permissions, encrypting sensitive information, and avoiding hardcoding confidential data directly in test plans.
Secure handling of parameter files ensures compliance with data protection policies and maintains the integrity of testing environments.
Validating Extracted Values
Validating the accuracy of extracted dynamic values is critical to ensure reliable test execution. Testers should verify that the correlation logic correctly captures the necessary parameters from server responses and that these values are properly passed to subsequent requests.
Adding assertions or debug samplers can help detect extraction errors early, preventing cascading failures in the test flow.
Reusability and Maintainability of Test Scripts
Creating reusable and maintainable test scripts improves efficiency and reduces manual errors over time. Organizing test plans into modules container inside or using controllers like the module controller and the first parameterized controller allows for better management of repeating sequences and different parameters. The module controller is a key component that helps reference and execute specific modules within the test plan, enhancing modularity. The parameterized controller is especially useful for running the same action with different parameters, making it easier to handle complex test scenarios. By leveraging the parameterized controller and module controller together, testers can modularize their scripts and reuse components effectively, enhancing scalability and maintainability. In more advanced scenarios, using a second parameterized controller enables running multiple sets of parameters independently, further increasing flexibility and control over test execution.
Additionally, documenting variables, correlation rules, and the use of the parameterized controller facilitates easier updates and future use, making the test scripts scalable for load testing scenarios.
About QSS
QSS Technosoft is a leading provider of Quality Assurance and Testing services in India and having a proven track executing enterprise level web and mobile applications for its esteemed customers. QSS has a test center of excellence with a dedicated and experienced team of QAengineers.
How QSS Technosoft Helps
- Expertise in Performance Testing with JMeter: Skilled in designing and executing thorough performance tests using JMeter to ensure application robustness.
- Implementing End-to-End Parameterization & Correlation Strategies: Developing dynamic test scripts that handle unique user data and dynamic server responses effectively.
- Delivering Scalable, Optimized, and Reliable Test Scripts for Enterprises: Creating maintainable scripts that can handle high loads and complex scenarios for enterprise applications.
- Support for Continuous Performance Monitoring: Providing ongoing monitoring services to track application performance and promptly identify issues throughout the software lifecycle.
About Author
Prakhar Saxena is a Sr. QA Engineer currently working with QSS Technosoft Pvt Ltd. He has completed his Bachelor's degree in Information Technology.
Conclusion
Parameterization and correlation are two important processes in JMeter that ensure your performance tests are realistic and reliable. Parameterization allows you to simulate multiple users with different input data by replacing hard-coded values with variables, while correlation handles dynamic values like session IDs and authentication tokens returned by the server during test execution.
Mastering both parameterization and correlation enables you to create robust test scripts that closely mimic real-world user behavior, leading to more accurate and meaningful load testing results and reliable test results. This reduces manual errors, improves test scalability, and helps identify genuine performance bottlenecks.
For businesses aiming to optimize their applications under load, leveraging expert help in implementing effective parameterization and correlation strategies can significantly enhance test quality and efficiency. Investing in professional guidance ensures your performance testing delivers reliable insights to support informed decision-making.
Contact us now .Partner with QSS Technosoft to maximize the effectiveness of your JMeter parameterization and correlation strategies for superior test outcomes.
FAQs Section
Q :What is the difference between parameterization and correlation in JMeter?
Parameterization involves replacing hard-coded input values in test scripts with variables to simulate multiple users or scenarios using different data sets. Correlation, on the other hand, focuses on capturing dynamic values like session IDs or authentication tokens from server responses and using them in subsequent requests to maintain valid sessions during test execution.
Q :How does CSV Data Set Config work in parameterization?
CSV Data Set Config reads data from an external CSV file and assigns the values to variables that can be used in test scripts. This allows JMeter to run tests with multiple users or different inputs by fetching values like usernames and passwords dynamically during execution.
Q: Which extractor is best for correlation in JMeter?
The Regular Expression Extractor is widely used for correlation, as it allows you to parse response data using defined patterns to capture dynamic values. For JSON responses, the JSON Extractor is preferable, while Boundary Extractor can be useful when patterns are difficult to define but boundaries are consistent.
Q :Can correlation errors affect test accuracy?
Yes, missing or incorrect correlation can cause test scripts to fail or produce unreliable results because dynamic values like session IDs or tokens are not properly handled. This leads to invalid sessions or authentication failures, impacting the accuracy and reliability of performance tests.
Q :Why choose QSS Technosoft for JMeter testing services?
QSS Technosoft offers expertise in performance testing with JMeter, providing end-to-end parameterization and correlation strategies. Their scalable and optimized test scripts reduce manual errors and improve test reliability. With continuous performance monitoring and experienced QA engineers, QSS ensures superior test outcomes that help businesses make informed decisions.
How to Handle Parameterization and Correlation in JMeter?